Escape Sequences
In this tutorial, we will understand the use and importance of escape sequences in the C programming language.
In this tutorial, we will understand the use and importance of escape sequences in the C programming language.
Escape sequences in C are special characters that we use to represent certain characters that we can’t directly type on a regular keyboard. These characters are either non-printable or have special meanings. We use escape sequences to format strings in specific ways or to include characters that aren’t normally allowed within a string.
To indicate that we’re using an escape sequence, we start with a backslash (\) followed by a specific character or combination of characters.
The following table shows the list of most commonly used escape sequences in C:
| Escape Sequence | Name |
|---|---|
| \n | Newline character |
| \t | Horizontal tab |
| \b | Backspace |
| \r | Carriage return |
| \” | Double quote |
| \’ | Single quote |
| \\ | Backslash |
Let’s see these characters in action.
The newline character is used to move the cursor at the beginning of the next line.
For example:
printf(“Hello!\nI am John.”);Output:
Hello!
I am John.Tab (\t) represents the horizontal tab character and is used to insert a horizontal tab.
For example:
printf(“Hello!\tI am John.”);Output:
Hello! I am John.Backspace (\b) is used to move the cursor back one position.
For example:
printf(“Hello!\b I am John.”);Output:
Hello I am John.Carriage return (\r) is used to move the cursor at the beginning of the current line.
For example:
printf(“Hello!\rI am John.”);Output:
I am John.Double quote (\”) is used to include a double quote within a string as simply adding a double quote within a string is not allowed.
For example:
printf(“I love the \”C programming\” language.”);Output:
I love the “C programming” language.Single quote (\’) is used to include a single quote within a string as simply adding a single quote within a string is not allowed.
For example:
printf(“I love \’C\’.”);Output:
I love ‘C’.Backslash (\\) is used to include a backslash within a string.
For example:
printf(“Path: C:\\Programs”);Output:
Path: C:\ProgramsFollowing are some extra escape sequences which are good to know:
The \a character is used to generate a beep sound.
For example, the following program when executed will generate a beep sound after printing the output.
int main()
{
printf("I love C\a.");
return 0;
}The question mark (\v?) character is used to display a question mark symbol within a string.
For example:
printf("What is 2 + 2\?");Output:
What is 2 + 2?The octal number escape sequence (\0oo) allows you to specify a character using its octal value. The ‘oo’ represents one to three octal digits (0-7), which correspond to the character’s ASCII code.
For example:
printf("The character with octal value \\051 is ‘%c’", ‘\051’);Output:
The character with octal value \051 is ')'We are getting the above output because the octal value ‘\051’ represents the ASCII code for the character ‘)’. This can be checked in the following ASCII table:
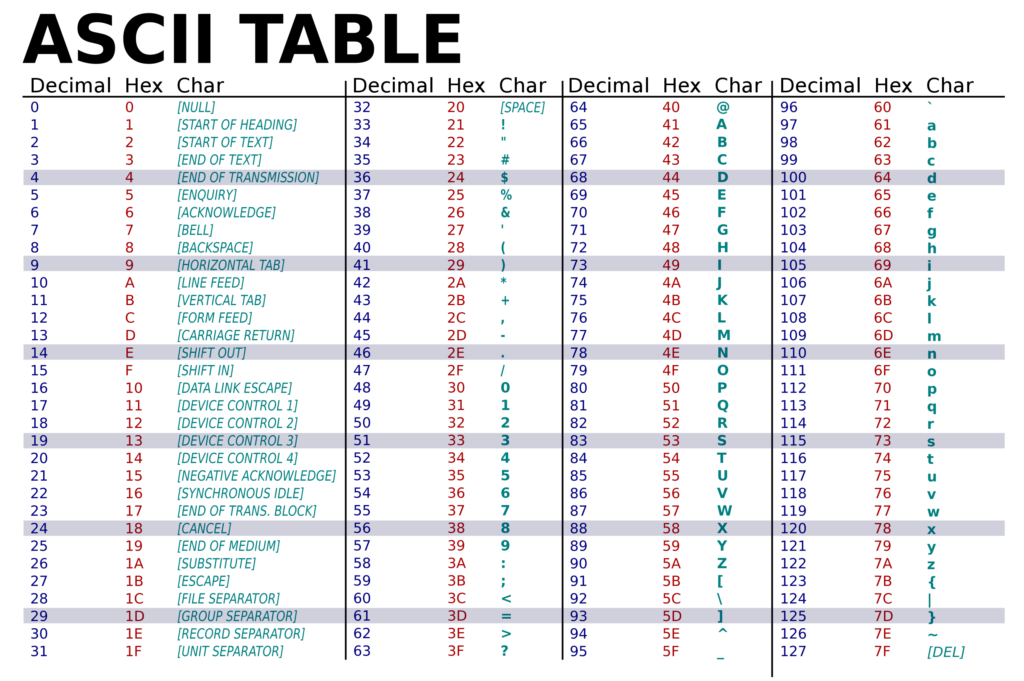
The decimal equivalent of the octal number 51 is 41. Therefore, character ‘)’ lies in row 41.
The hexadecimal number escape sequence (\xhh) allows you to specify a character using its hexadecimal value. The ‘hh’ represents one to two hexadecimal digits (0-9, A-F or a-f), which correspond to the character’s ASCII code.
For example:
printf("The character with hexadecimal value \\x41 is '%c'", '\x41');Output:
The character with hexadecimal value \x41 is 'A'The NULL escape sequence (\0) is used to represent the null character. It has a value of 0 and is often used to terminate strings in C.
For example:
printf("Hello\0World!");Output:
HelloIn the output, the string is terminated after the character ‘o’ because \0 represents the null character and indicates the end of the string. So, no character will be displayed after the null character.
This tutorial has provided an overview of escape sequences in the C programming language and their importance. Escape sequences are special characters used to represent non-printable characters or characters that can’t be directly typed on a keyboard. They are used for formatting strings and including special characters within them.
We have learned some commonly used escape sequences like:
and we have learned some not so common escape sequences as well:
Overall, the tutorial serves as a handy reference for understanding and working with escape sequences in C.
Leave a comment