Integer Data Type with Long Long Modifier
In this tutorial, we will learn about the long long modifier used with integer data types, and understand its purpose and importance.
In this tutorial, we will learn about the long long modifier used with integer data types, and understand its purpose and importance.
A modifier is used to change or modify the type of something. There are different types of modifiers that can be used with integers:
These modifiers can be added before an integer type to change its default size and range.
The detailed explanation of short modifier is available in this article and the explanation on long modifier is available in this article.
The long long modifier was added to support larger integers, as there was a growing demand for it in the community. It is designed to hold at least a 64-bit wide integer.
To declare a variable with the long long modifier for signed integers, you can use the following syntax:
long long int variable_name;OR
int long long variable_name;Here is an example program that uses the long long modifier:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
long long int var = -987645984245924924;
printf("The integer value stored in variable var is %lld and ", var);
printf("the size of long long integer in my machine is %d bytes", sizeof(var));
}Output:

Please note that on my machine, the size of a long long int is 8 bytes, which corresponds to 64 bits.
We can also calculate the range of a long int using the following formula:
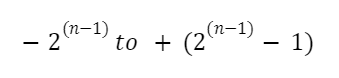
where n represents the number of bits.
For example, a long int with 4 bytes (32 bits) has the following range:
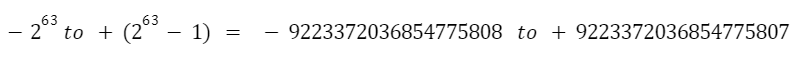
The long long modifier can also be used with unsigned integers. The syntax for declaring a variable with the long long modifier for unsigned integers is as follows:
unsigned long long int variable_name;OR
unsigned int long long variable_name;Here is an example program that uses the long long modifier for unsigned integers:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
unsigned long long int var = 198734894381297391;
printf("The integer value stored in variable var is %llu and ", var);
printf("the size of unsigned long integer in my machine is %d bytes", sizeof(var));
}Output:

The range of an unsigned long int with 8 bytes (64 bits) is:

That’s the explanation of the long long modifier and its usage with integer data types.
Leave a comment